Electrophoresis Definition:
It is a separation technique which involves the
migration of charged particles through liquid or semi solid gel medium under the
influence of electric field.
Apparatus:
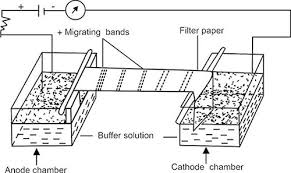
Electrolytic solution or buffer solution
Electric field or battery (anode/cathode)
Charged molecules of biological interest such as
DNA, RNA and protein.
The porous jelly-like material fills in the
electrophoretic tank on which the sample mixture placed. The sample mixture
moves through the pores to their respective charges. Three different types of
supporting media are mostly used.
·
Filter paper
·
Cellulose acetate
·
Gel media
Filter paper
Filter paper is made up of cellulose. It contains 95
to 96% cellulose otherwise it is impure. It was commonly used supporting media
before 1950s.
It is used by moisten the filter paper by buffer solution
and works as a junction between two half cells. The sample is placed in the
filter that show the movement of ions towards their respective electrode when
the electric field is applied.
It is used to separate carbohydrates, lipids,
proteins and enzymes.
Disadvantages:
Due to thin
nature of filter paper, it may be tore.
Their uneven size cause poor separation.
Cellulose acetate
It is better than filter paper. Cellulose is formed
due to the polymerization of glucose.
Cellulose acetate have 2 or 3 % acetate group per
unit glucose molecule.
Its absorptive capacity is less than filter paper
and expensive than filter paper.
It is commonly used in clinical and forensic laboratories
for separation of protein.
Gel
Media:
Gel may be viscous liquid or semisolid. These type
of gel is prepared with the help of steps given below:
Take solid form such as Polyacrylamide, Starch
orAgar and heat it with water.
This will become liquid and pour it in the mould of
your own choice.
There are
three different types of gel are used in electrophoresis process such as Polyacrylamide
gel, Starch gel & Agarose gel.
Polyacrylamide Gel:
It has small pore size. There are two types of poly
acrylamide gel. Cationic gel is acidic in nature having pH less than 7. Anionic
gel is basic in nature having pH greater than 7.
It is use for the analysis of Protein, carbohydrate,
isoenzyme and measurement of DNA.
Starch Gel
A large number of glucose molecules unite to form
starch and polysaccharide. It is commonly prepared by potato. Starch gel is
prepared by heating 10-12% in water.
It is use for the analysis of protein and isoenzyme.
It is commonly used supporting media in
electrophoresis. It is the mixture of polysaccharide (glycogen, cellulose),
principally agarose or agropectin.
It has big pore size. It is use to separate high
molecular weight molecules. It is use to separate the fragment of DNA and
protein.








0 Comments